Hippo on Land
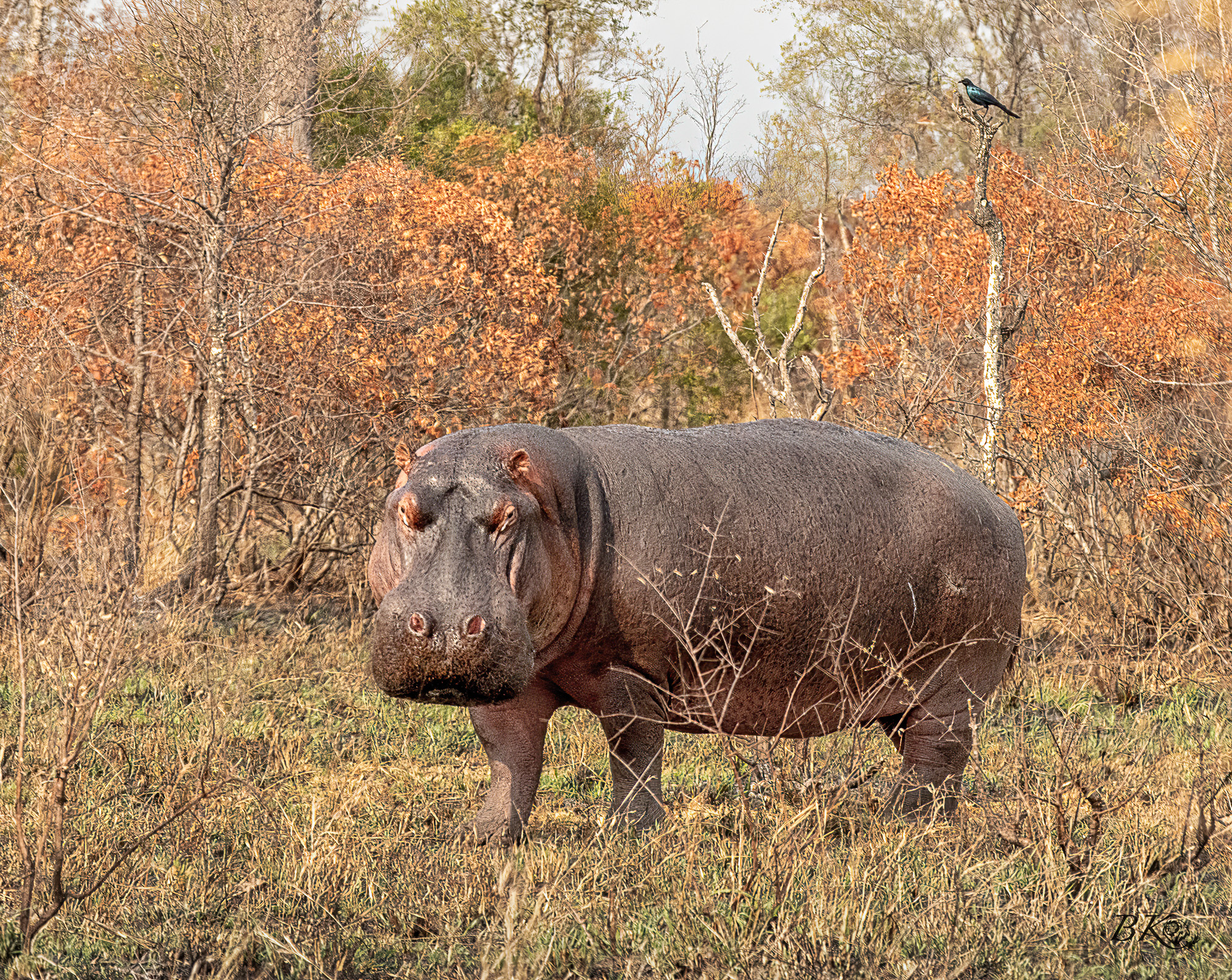

By night, hippos walk along familiar paths as far as 6 miles into surrounding grasslands to feed for five or six hours. Hippos, however, eat relatively little vegetation for their size (about 80 pounds per night), as their energy requirement is low because they are buoyed in warm water much of the time. We saw this hippo midmorning, which is quite unusual.
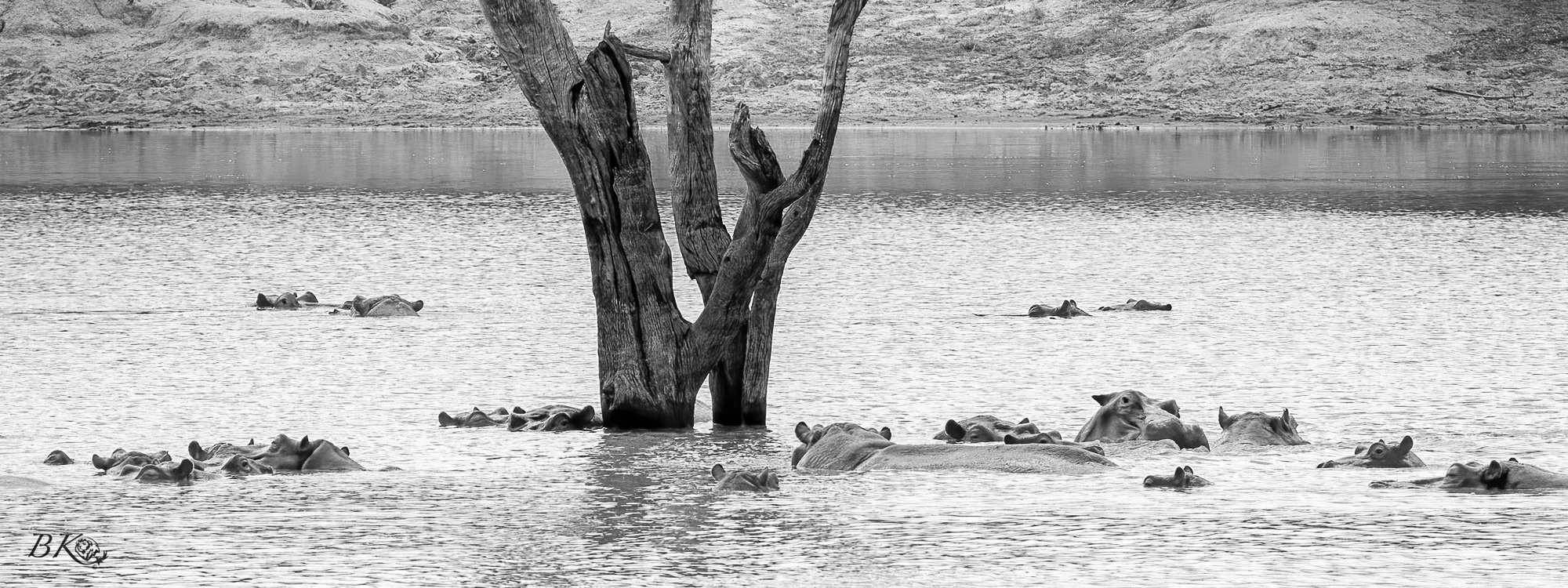
 Hippos are the third-largest living land mammal, after elephants and white rhinos. Its name comes from the ancient Greek for “river horse.” Hippos rely on water or mud to keep cool — this accounts for the amount of time they spend in the water. Instead of sweating, they secrete a viscous red fluid, which protects the animal’s skin against the sun and possibly acts as healing agents.
Hippos are the third-largest living land mammal, after elephants and white rhinos. Its name comes from the ancient Greek for “river horse.” Hippos rely on water or mud to keep cool — this accounts for the amount of time they spend in the water. Instead of sweating, they secrete a viscous red fluid, which protects the animal’s skin against the sun and possibly acts as healing agents.






